
The P wave in lead V1 is usually negative. Thus paradoxically, some drugs used to slow the heart rate may in fact end up increasing it! This can have dangerous consequences.Ītypical atrial flutter ( Table 44.1) is a rare rhythm disturbance, recognized when the deflections in the inferior leads are positive (probably as the circuit proceeds in a clockwise rotation, rather than the anti-clockwise motion of typical atrial flutter). Sometimes anti-arrhythmic drugs (such as propafenone) can slow the atrial rate, say to 250 b/min, sufficient for the AV node to allow 1 to 1 conduction. If the rate of transmission is (in the absence of anti-arrhythmic drugs) less than this, say 1 in 5 or 1 in 6, then there is a high probability that there is also intrinsic conducting tissue disease. Sometimes the conduction is 1 in 3 or 4, giving a QRS rate respectively of 100 and 75 b/min. This has led to an aphorism in arrhythmology whenever a tachycardia is seen with a heart rate of exactly 150 b/min, the rhythm disturbance is atrial flutter until proved otherwise.
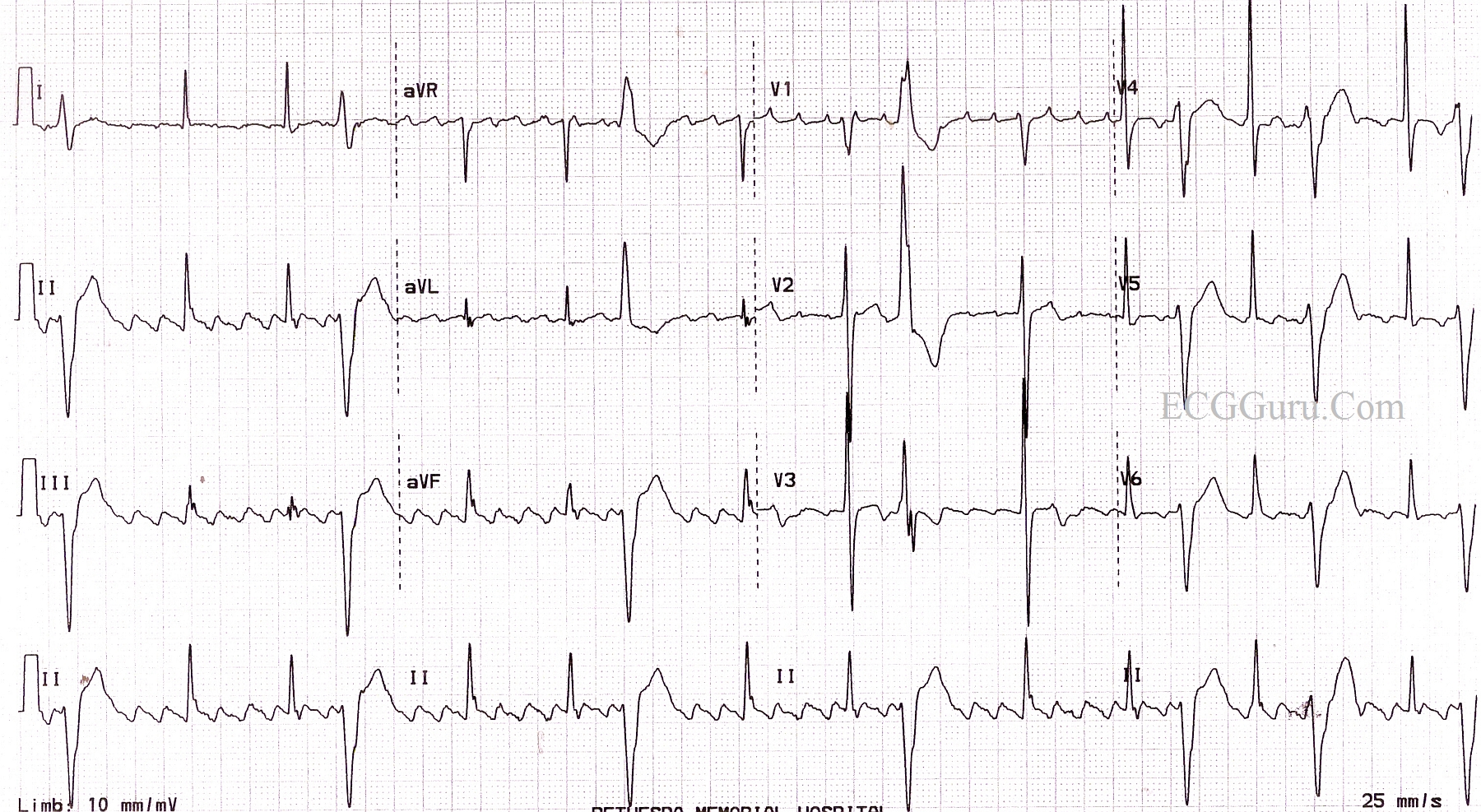
This is too fast for the atrioventricular (AV) physiologically to allow for 1 to 1 conduction down to the ventricles, and usually a fixed proportion of beats get through, often one in two, giving a QRS (and hence heart) rate of 150 b/min. The right atrial circuit is usually of such a length that 300 circuits occur per minute. Occasionally the P waves in lead V1 are not well developed. P wave activity is often reasonably well seen in lead V1, when it is predominantly positive. The ‘sawtooth’ baseline typically has a slow downstroke and a rapid upstroke. 44.1a– d) and results in a highly characteristic ECG appearance, with continual electrical activity best seen in the inferior leads. It is due to a macro re-entrant circuit in the right atrium ( Fig. Other resources: Refer to our other post on atrial tachycardia.Atrial flutter is a common arrhythmia, especially in men (perhaps as they have larger hearts) ( Table 44.1). However, compared to atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter is often more difficult to rate control and is more responsive to cardioversion and EP ablation. Atrial flutter is managed similarly to atrial fibrillation with rate control and anticoagulation. This case demonstrates the result of atrial flutter conducted at variable 3:1 and 4:1 due to the patient taking metoprolol at baseline. An abrupt and fixed SVT at a rate of 150bpm should always raise suspicion for atrial flutter and can be effectively identified with vagal maneuvers or imitation of AV nodal blockade. In the setting of a healthy AV node and no pharmacologic AV nodal blockade this the atrial rate is typically conducted at a 2:1 producing a ventricular rate of ~150bpm.


This typically produces an atrial rate ~300bpm with a negative ‘sawtooth’ deflection in lead II. Teaching: Atrial flutter is due to a large re-entry circuity, through the cavo-tricuspid isthmus (CTI). Official ECG Read: Typical atrial flutter with variable conduction of 3:1 and 4:1 at a ventricular rate of ~75. Advance through the animations to highlight the abnormalities and final diagnosis. Then ask them to commit to a specific diagnosis. If they do not do so on their own, prompt them to point out the distinguishing characteristics (mostly regular, atrial rate ~300bpm) of this SVT.

Have one learner provide a systematic interpretation of the ECG. Have the image pulled up on the presenting screen or monitor. Plan to spend 5-15 minutes familiarizing yourself with the ECG and relevant background information.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
